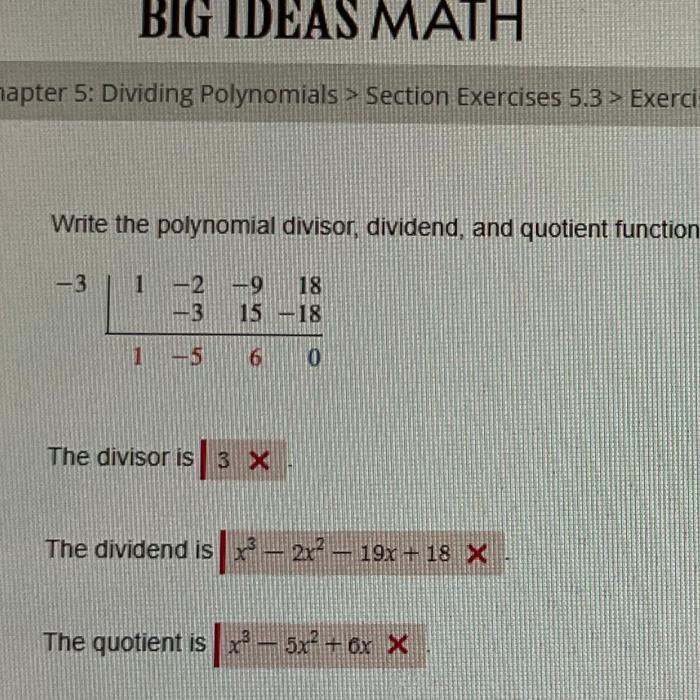
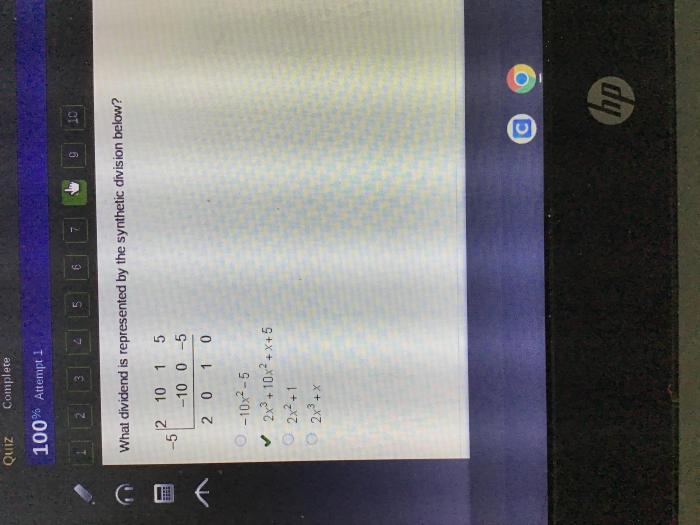
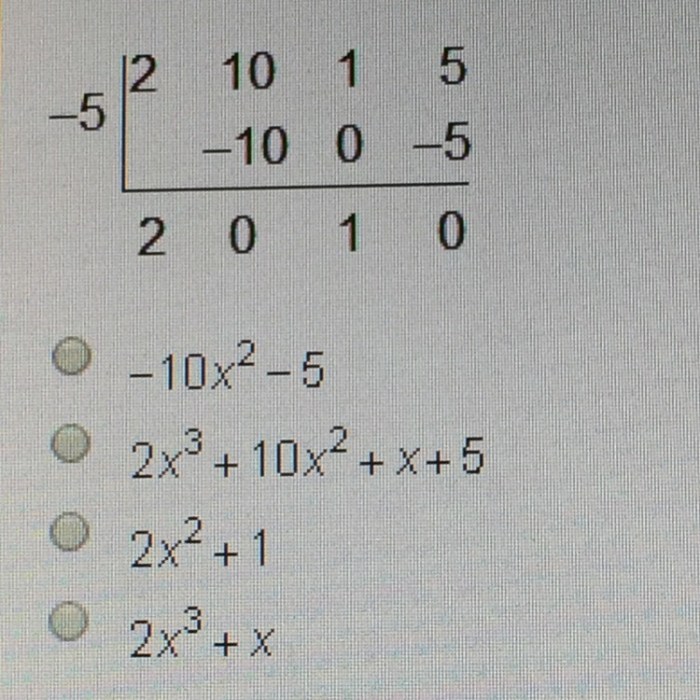What dividend is represented by the synthetic division below – In the realm of mathematics, synthetic division emerges as a powerful tool for simplifying polynomial equations. This technique, when applied to a dividend, unveils valuable insights into its structure and behavior. Delve into this comprehensive guide to unravel the intricacies of synthetic division and uncover the dividend it represents.
Synthetic division streamlines the process of dividing polynomials, making it an indispensable technique in various mathematical applications. By understanding the dividend’s role in this division method, we gain a deeper appreciation for its significance in polynomial operations.
Synthetic Division: What Dividend Is Represented By The Synthetic Division Below
Synthetic division is a mathematical technique used to divide a polynomial by a linear factor of the form (x – a) without performing the traditional long division algorithm. It simplifies the process of polynomial division, making it faster and easier to perform.
Dividend in Synthetic Division
In synthetic division, the dividend is the polynomial that is being divided. It is represented by a list of coefficients, starting with the highest-degree term and ending with the constant term. For example, the dividend 3x 2– 5x + 2 would be represented as [3, -5, 2].
Synthetic Division Process
The synthetic division process involves dividing the first coefficient of the dividend by the coefficient of the linear factor (a). The quotient is written below the dividend, and the product of the quotient and the linear factor is subtracted from the dividend.
This process is repeated until all coefficients of the dividend have been used.
Representation of Dividend in Synthetic Division Notation, What dividend is represented by the synthetic division below
In synthetic division notation, the dividend is represented by a row of coefficients with a vertical line to the left. The coefficients are arranged in descending order of degree, with the constant term on the right. For example, the dividend 3x 2– 5x + 2 would be written as:
“`| 3
5 2 |
“`
Examples and Applications
Synthetic division is used in various mathematical applications, including:
- Solving polynomial equations
- Evaluating polynomials at specific values
- Finding zeros of polynomials
For example, synthetic division can be used to solve the equation x 3– 2x 2– 5x + 6 = 0. By dividing the polynomial by (x – 2), we obtain the quotient x 2– 4x + 3 and the remainder 0. This means that (x – 2) is a factor of x 3– 2x 2– 5x + 6, and the roots of the polynomial are x = 2, x = 2 ± i√7.
Quick FAQs
What is the purpose of synthetic division?
Synthetic division simplifies the division of polynomials, making it easier to find roots and factors.
How is the dividend represented in synthetic division?
The dividend is represented by the coefficients of its terms, arranged in descending order of exponents.
What is the significance of the coefficients in the dividend?
The coefficients determine the shape and behavior of the dividend polynomial.