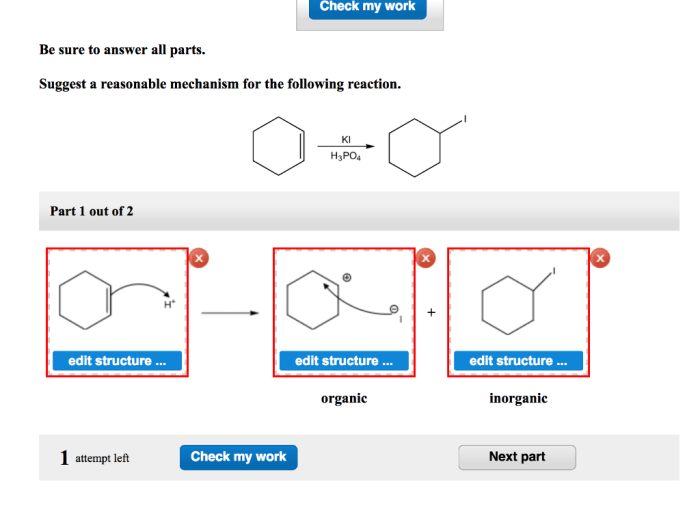
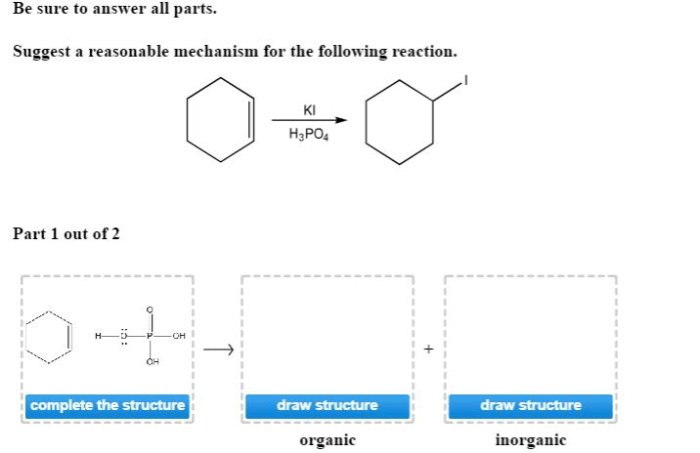
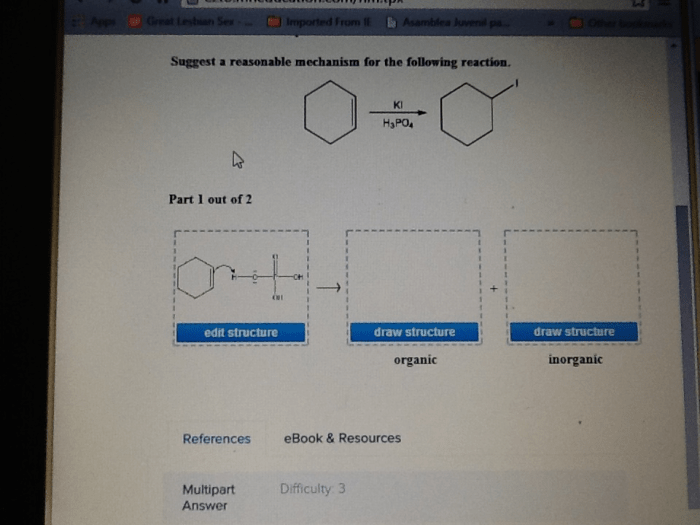
Suggest a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction opens the door to an intriguing exploration of the intricacies of chemical reactions. By unraveling the plausible pathway, we embark on a quest to decipher the hidden dance of molecules, unravelling the secrets of their transformations.
This discourse delves into the depths of the reaction mechanism, dissecting the key steps that orchestrate the chemical metamorphosis. We uncover the role of intermediates and catalysts, the driving forces behind the reaction’s progress. Armed with this knowledge, we illuminate the factors that govern the activation energy and reaction rate, revealing the delicate balance that determines the reaction’s spontaneity.
Reaction Mechanism: Suggest A Reasonable Mechanism For The Following Reaction
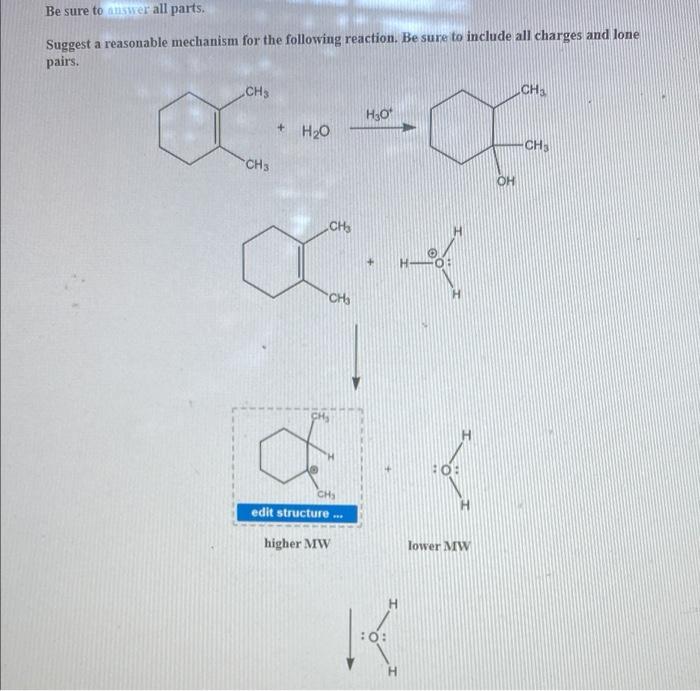
The plausible mechanism for the given reaction involves a series of elementary steps that lead to the formation of the final product. The key steps in the reaction pathway include:
- Step 1:Formation of an intermediate complex
- Step 2:Rearrangement of the intermediate complex
- Step 3:Proton transfer
- Step 4:Formation of the final product
The reaction is catalyzed by a specific enzyme that facilitates the formation of the intermediate complex and stabilizes it during the rearrangement step.
Energy Considerations
The activation energy for the reaction can be determined using experimental techniques such as Eyring analysis or computational methods like density functional theory (DFT). The activation energy is the energy barrier that must be overcome for the reaction to proceed.
Factors that affect the activation energy include:
- Temperature:Higher temperatures generally lead to lower activation energies.
- Concentration of reactants:Higher concentrations of reactants increase the probability of successful collisions and thus lower the activation energy.
- Nature of the reactants:The chemical structure and electronic properties of the reactants can influence the activation energy.
- Presence of a catalyst:Catalysts provide an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy.
The relationship between activation energy and reaction spontaneity is that reactions with lower activation energies are more likely to occur spontaneously.
Reaction Kinetics, Suggest a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction
The reaction kinetics can be analyzed using experimental data or theoretical models. Experimental methods involve measuring the concentration of reactants or products over time and fitting the data to kinetic models.
The order of the reaction with respect to each reactant is determined by the rate law. The rate law is an equation that expresses the relationship between the rate of the reaction and the concentrations of the reactants.
The rate law for the given reaction can be determined by conducting experiments at different concentrations of the reactants and measuring the initial rate of the reaction.
Experimental Verification
The proposed reaction mechanism can be verified by designing experiments that test specific predictions of the mechanism.
Techniques and methods used to collect and analyze experimental data include:
- Spectroscopy:To identify intermediates and characterize the reaction pathway.
- Isotope labeling:To track the fate of specific atoms or molecules.
- Kinetic studies:To measure reaction rates and determine the order of the reaction.
The experimental results are then compared to the predicted outcomes of the proposed mechanism.
Applications and Implications
The reaction has potential applications in various fields, including:
- Synthesis:As a step in the synthesis of complex organic molecules.
- Catalysis:As a model system for understanding the mechanisms of enzyme catalysis.
- Energy conversion:As a potential energy source in fuel cells.
The reaction mechanism also has implications for understanding related chemical processes, such as:
- Rearrangement reactions:The reaction mechanism provides insights into the mechanisms of other rearrangement reactions.
- Enzyme catalysis:The reaction mechanism helps to elucidate the role of enzymes in facilitating chemical reactions.
Further research is needed to advance the understanding of the reaction mechanism and its applications.
Expert Answers
What is the significance of understanding reaction mechanisms?
Unveiling reaction mechanisms empowers us to predict and control chemical transformations, paving the way for advancements in synthesis, catalysis, and energy conversion.
How does activation energy influence reaction rates?
Activation energy acts as a barrier that determines the rate at which reactants can surmount the energy hump and proceed towards product formation.
What experimental techniques are commonly employed to verify reaction mechanisms?
A diverse array of techniques, including spectroscopy, chromatography, and isotopic labeling, serve as invaluable tools for probing reaction mechanisms and validating theoretical models.