Ecological community like a tundra or coral reef – Ecological communities like a tundra or coral reef stand as mesmerizing testaments to the intricate tapestry of life on Earth. These biomes, vastly different yet equally captivating, serve as microcosms of the remarkable diversity and resilience of our planet’s ecosystems.
From the icy expanse of the tundra to the vibrant depths of the coral reef, this narrative delves into the defining characteristics, unique adaptations, and delicate balance that shape these extraordinary communities.
Define Ecological Community
An ecological community is a group of living organisms that share a common environment and interact with each other in various ways.
Characteristics of an ecological community include:
- Co-existence: Species live together in the same area.
- Interdependence: Species rely on each other for food, shelter, and other resources.
- Competition: Species compete for resources such as food, water, and space.
- Predation: Species prey on each other for food.
Examples of ecological communities include forests, grasslands, deserts, and coral reefs.
Describe the Tundra

The tundra is a cold, treeless region found in the Arctic and Antarctic.
Physical Characteristics
- Low temperatures: Average temperatures below freezing for most of the year.
- Permafrost: Soil that remains frozen year-round.
- Short growing season: Limited plant growth during the brief summer months.
- Sparse vegetation: Mosses, lichens, and small shrubs.
Flora and Fauna, Ecological community like a tundra or coral reef
- Plants: Adapted to cold temperatures and short growing seasons.
- Animals: Migratory birds, mammals (e.g., reindeer, polar bears), and insects.
Adaptations of Organisms
- Thick fur or feathers for insulation.
- Migration to warmer climates during winter.
- Short life cycles to reproduce quickly during the short growing season.
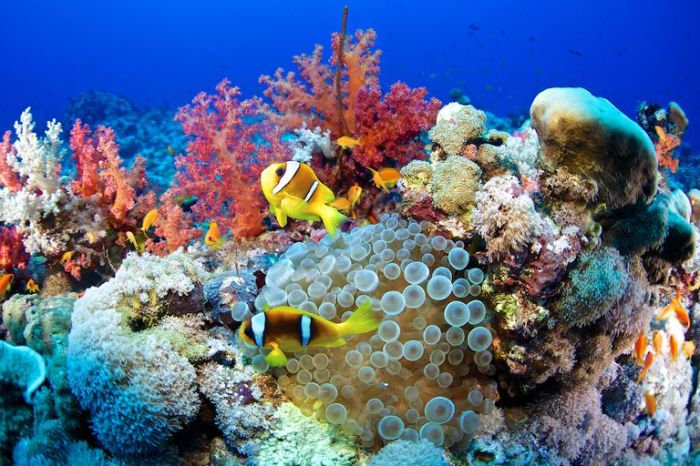
Describe the Coral Reef
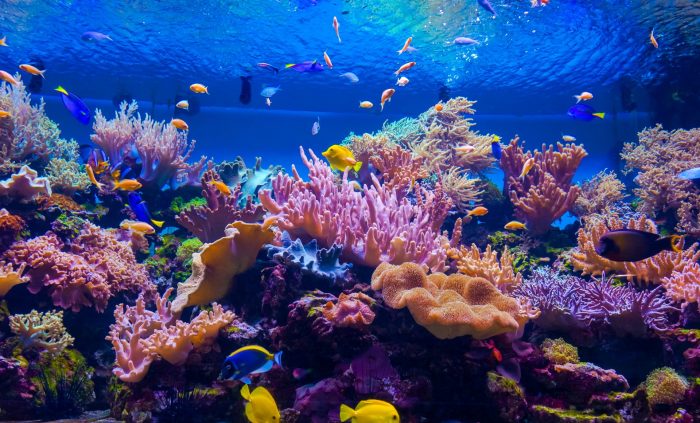

A coral reef is a diverse underwater ecosystem found in warm, shallow waters.
Physical Characteristics
- Clear, tropical waters.
- Coral colonies: Made up of tiny animals called polyps.
- Limestone structure: Formed from the calcium carbonate secreted by corals.
- High biodiversity: Supports a wide variety of marine life.
Flora and Fauna, Ecological community like a tundra or coral reef
- Corals: Provide the foundation of the reef.
- Algae: Live in symbiosis with corals and provide food.
- Fish: Diverse array of species, including predators, herbivores, and scavengers.
Symbiotic Relationships
- Coral-algae symbiosis: Algae provide food, while corals provide protection.
- Cleaner fish-host relationships: Cleaner fish remove parasites from larger fish.
Compare and Contrast the Tundra and Coral Reef: Ecological Community Like A Tundra Or Coral Reef

| Tundra | Coral Reef | |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Characteristics | Cold temperatures, permafrost, sparse vegetation | Warm waters, coral colonies, high biodiversity |
| Flora and Fauna | Mosses, lichens, reindeer, polar bears | Corals, algae, fish, cleaner fish |
| Adaptations of Organisms | Thick fur, migration, short life cycles | Symbiotic relationships, camouflage, protective coloration |
Threats to Ecological Communities
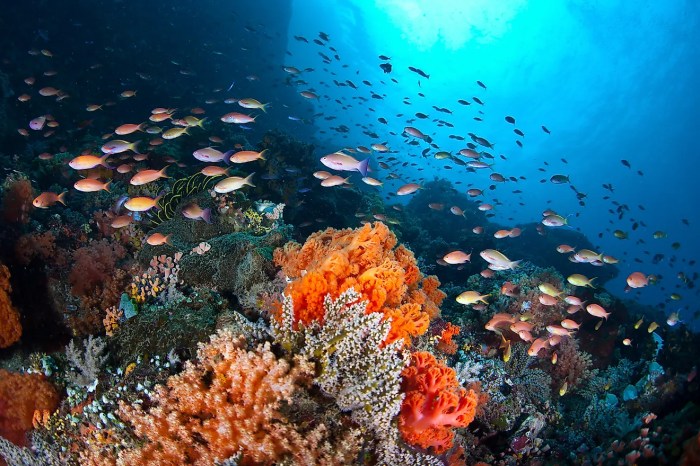

Ecological communities face various threats, including:
- Habitat loss and fragmentation.
- Pollution and climate change.
- Invasive species.
- Overexploitation of resources.
Human activities can have significant impacts on ecological communities, such as:
- Deforestation.
- Water pollution.
- Climate change.
- Overfishing.
Question Bank
What is an ecological community?
An ecological community refers to a group of interacting organisms living in a specific environment, forming a self-sustaining system with unique characteristics.
How do organisms adapt to the extreme conditions of the tundra?
Organisms in the tundra have evolved adaptations such as thick fur, specialized feeding strategies, and reduced surface area to conserve heat and survive the harsh cold.
What is the significance of symbiotic relationships in coral reefs?
Symbiotic relationships, such as the mutualistic partnership between corals and algae, are crucial for the survival and growth of coral reefs, providing nutrients and protection.