Rank the following solutions from lowest to highest vapor pressure. This article explores the concept of vapor pressure and its significance in solutions. We will discuss the factors influencing vapor pressure, the relationship between solute concentration and vapor pressure, and establish criteria for ranking solutions based on their vapor pressure.
Vapor pressure plays a crucial role in various scientific fields and practical applications. Understanding the principles of vapor pressure enables us to solve real-world problems and make informed decisions in chemistry, engineering, and other disciplines.
Vapor Pressure
Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in equilibrium with its liquid or solid phase. It is a measure of the tendency of a substance to evaporate or sublime. The higher the vapor pressure, the more volatile the substance.
Vapor pressure is an important property in many fields, including chemistry, engineering, and environmental science. It is used to design distillation columns, calculate boiling points, and predict the behavior of volatile materials.
Factors Affecting Vapor Pressure
- Temperature:Vapor pressure increases with temperature. This is because the higher the temperature, the more energy the molecules have, and the more likely they are to escape from the liquid or solid phase.
- Molecular structure:Vapor pressure is also affected by the molecular structure of the substance. In general, substances with weaker intermolecular forces have higher vapor pressures. For example, water has a higher vapor pressure than benzene because the hydrogen bonds in water are weaker than the van der Waals forces in benzene.
Solutions and Vapor Pressure
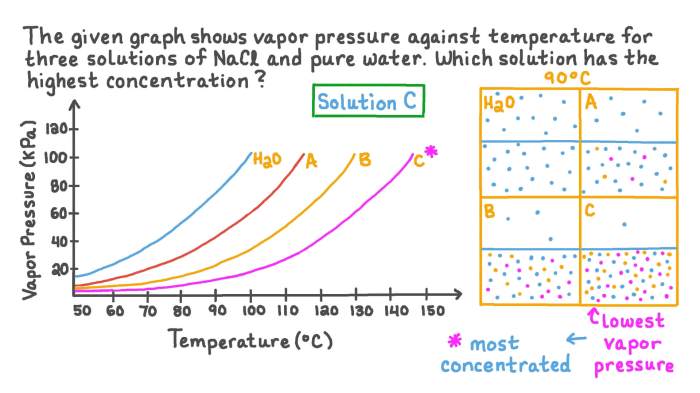
The vapor pressure of a solution is lower than the vapor pressure of the pure solvent. This is because the solute particles compete with the solvent particles for space in the vapor phase. The more solute particles there are in the solution, the lower the vapor pressure.
The relationship between vapor pressure and solute concentration is linear. This means that the vapor pressure of a solution decreases linearly as the solute concentration increases.
Examples of Solutions with Varying Vapor Pressures, Rank the following solutions from lowest to highest vapor pressure.
- Water:Water has a vapor pressure of 23.76 mmHg at 25 °C.
- Seawater:Seawater has a vapor pressure of 22.99 mmHg at 25 °C.
- Ethanol:Ethanol has a vapor pressure of 43.9 mmHg at 25 °C.
Ranking Solutions

Solutions can be ranked from lowest to highest vapor pressure based on their solute concentration. The more concentrated the solution, the lower the vapor pressure.
| Solution | Solute Concentration (M) | Vapor Pressure (mmHg) |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 0 | 23.76 |
| Seawater | 0.5 | 22.99 |
| Ethanol | 1.0 | 43.9 |
The table shows that water has the highest vapor pressure, followed by seawater and ethanol. This is because water has the lowest solute concentration, followed by seawater and ethanol.
Applications of Vapor Pressure
Vapor pressure has a wide range of applications in various fields, including chemistry, engineering, and environmental science.
- Chemistry:Vapor pressure is used to design distillation columns, calculate boiling points, and predict the behavior of volatile materials.
- Engineering:Vapor pressure is used to design heat exchangers, evaporators, and other equipment that handles volatile materials.
- Environmental science:Vapor pressure is used to predict the behavior of volatile pollutants in the atmosphere.
Vapor pressure is a valuable tool that can be used to solve a variety of practical problems. By understanding the factors that affect vapor pressure, scientists and engineers can design systems that safely and efficiently handle volatile materials.
Question Bank: Rank The Following Solutions From Lowest To Highest Vapor Pressure.
What is vapor pressure?
Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by the vapor of a substance in equilibrium with its liquid or solid phase.
How does temperature affect vapor pressure?
Vapor pressure increases exponentially with increasing temperature.
How does solute concentration affect vapor pressure?
Adding a non-volatile solute to a solvent lowers the vapor pressure of the solution.