For each statement describing hormonal effects, this comprehensive overview delves into the intricate world of hormones, exploring their profound impact on our physiological functions, behavior, and overall well-being.
From regulating metabolism and growth to maintaining homeostasis, hormones play a pivotal role in orchestrating the delicate balance of our bodies. Their interactions and feedback mechanisms ensure hormonal harmony, while imbalances can lead to a cascade of health concerns.
Physiological Effects of Hormones

Hormones play a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. They influence metabolism, growth, and reproduction, ensuring the proper functioning of the body.
Metabolic Regulation
- Insulin and glucagon regulate blood glucose levels, maintaining energy homeostasis.
- Thyroid hormones control metabolic rate, affecting body temperature and energy expenditure.
Growth and Development
- Growth hormone promotes skeletal and muscular growth during childhood and adolescence.
- Sex hormones regulate secondary sexual characteristics and reproductive development.
Reproduction
- Gonadotropins (FSH and LH) stimulate gamete production and reproductive organ function.
- Progesterone and estrogen prepare the uterus for pregnancy and maintain it during gestation.
Hormonal Interactions and Feedback Mechanisms: For Each Statement Describing Hormonal Effects

Hormones interact with each other and with other regulatory systems to maintain hormonal balance. Feedback mechanisms ensure that hormone levels are within optimal ranges.
Hormonal Interactions, For each statement describing hormonal effects
- Thyroid hormones stimulate the production of growth hormone.
- Estrogen inhibits the production of gonadotropins.
Feedback Mechanisms
- Negative feedback loops: Hormones inhibit their own secretion when levels are high.
- Positive feedback loops: Hormones stimulate their own secretion when levels are low.
Hormonal Disorders and Treatment
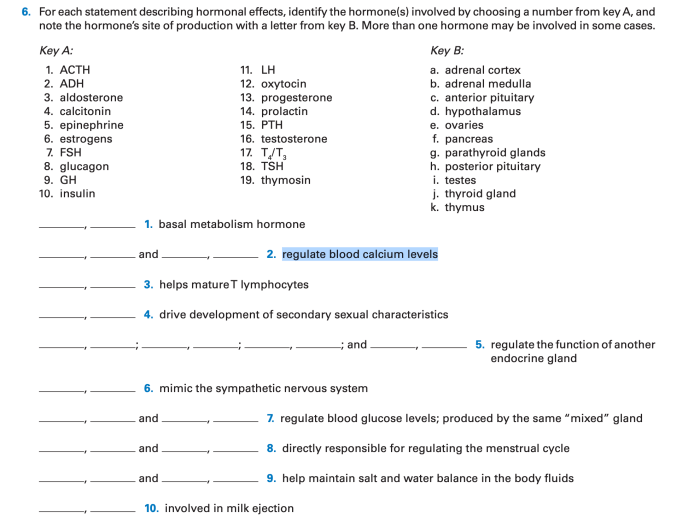
Hormonal imbalances can result in a range of disorders, affecting physical and mental health. Treatment options aim to restore hormonal balance.
Common Hormonal Disorders
- Diabetes mellitus: Insulin deficiency or resistance.
- Thyroid disorders: Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
- Cushing’s syndrome: Excessive cortisol production.
Treatment Options
- Hormone replacement therapy: Replenishing deficient hormones.
- Surgery: Removing tumors or overactive glands.
- Lifestyle modifications: Diet, exercise, and stress management.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the key physiological effects of hormones?
Hormones regulate metabolism, growth, reproduction, and maintain homeostasis, ensuring the proper functioning of various bodily systems.
How do hormones interact with each other?
Hormones interact through complex feedback mechanisms, ensuring hormonal balance. Positive feedback loops amplify hormonal signals, while negative feedback loops inhibit them, maintaining equilibrium.
What are common hormonal disorders?
Common hormonal disorders include diabetes, thyroid disorders, and polycystic ovary syndrome, resulting from imbalances in hormone production or function.